- Knee joint replacement
Knee joint replacement is a surgical replacement of the knee joint with an artificial joint, which fully replicates the anatomical elements of the human knee joint. This replacement allows the patient to perform all the essential movements without any feelings of pain or discomfort. Implantation of the artificial knee joint does not require a large bone resection, as the knee joints are preserved during the surgery. Some cases will require the ligament repair if they have been previously damaged.
How to know if you need a knee replacement surgery?
Knee joint replacement is performed when medication does not help with improving the overall knee condition. It is required when the medication does not improve pain relief even with the help of pain killers, as well as if there is a strong restriction in movement. These signs identify a damage in articular surfaces, meaning that you might need knee joint replacement, which aims to bring back a mobile and painless joint that will allow you to return to your usual lifestyle.
Before going into surgery, a consultation with a professional orthopedic surgeon is required. The doctor will determine the indications and contraindications for the joint replacement, by performing the necessary research and selection of the appropriate implants. X-ray examination will determine the condition of your joint and allow the doctor to make the exact and necessary measurements. You will be aware about all the possible risks and complications of the surgery.
The aims of the replacement:
disappearance of pain
restoration of limb function
restoration of the normal axis of the limb
restoration of full amplitude of movements
restoration of joint stability.
What are the indications for knee replacement?
Indications for knee replacement:
gonarthrosis with pronounced functional disorders, pain syndrome and malformed (valgus or viral) limb installation
aseptic necrosis of the femur
rheumatoid polyarthritis
Bekhterev's disease
consequences of trauma and osteosynthesis of the distal end of the thigh and the proximal end of the tibia (not earlier than 3 months after removal of metal structures)
Are there any contraindications for knee replacement?
Contraindications for knee replacement:
active infectious process
diseases of the cardiovascular and bronchial-pulmonary system in the stage of decompensation
the presence of foci of purulent infection in the body (tonsillitis, carious teeth, chronic sinusitis and otitis, purulent skin diseases, etc.)
lack of active extension in the knee joint
acute myocardial infarction and acute cerebral circulation within 1 year.
primary arthrodesis
acute thrombophlebitis
3-4 degrees of obesity
general somatic and mental illness in the acute stage.

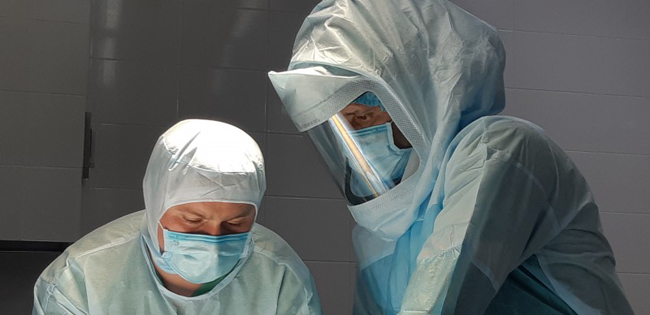
What are the types of knee joint replacement?
There are several classifications of knee replacement: they are divided into fixed and movable by the type of plastic liner used.
By the number of replaced articulated surfaces - single-click, bipolar and tripolar. According to another classification, the knee joints are separated.
They are:
unbound (low-congruent, non-stop device with posterior cruciate ligament retention)
semi-coupled (there is anteroposterior stabilization with replacement of the posterior cruciate ligament)
associated (with limited varus or valgus deviation and have rotation in the plane of bending)
hinges (having a rigid or rotary hinge with the possibility of moving in one plane)
Cement fixation of all components of the replacement is the "golden standard" of knee replacement. Cement-free fixation of components is possible, but less reliable than cement, and the cost of such implants is usually higher.
At the present stage, the requirements for knee joint replacement have increased significantly. They must:
replace the affected joint structures
keep intact joint structures
restore the physiological volume of movements
have a modular structure to solve various problems in the knee joint
optimize the axes of limb loading
be installed with simple operating techniques
have high mechanical resistance to wear
provide easy replacement of components.
The basis of any (biomechanical) classification of knee joint replacement is the degree of limitation of mobility in the sagittal and frontal plane, as well as the degree of connectivity of the femoral and tibial components.
How to determine which joint is best for me?
In each case there is an individual approach of implant selection for the patient.
What happens during the surgery?
Before the surgery, the patient undergoes a complete clinical examination (analysis, expert advice, anesthesiologist examination). Hospitalization of the patient takes place 1-2 days before surgery.
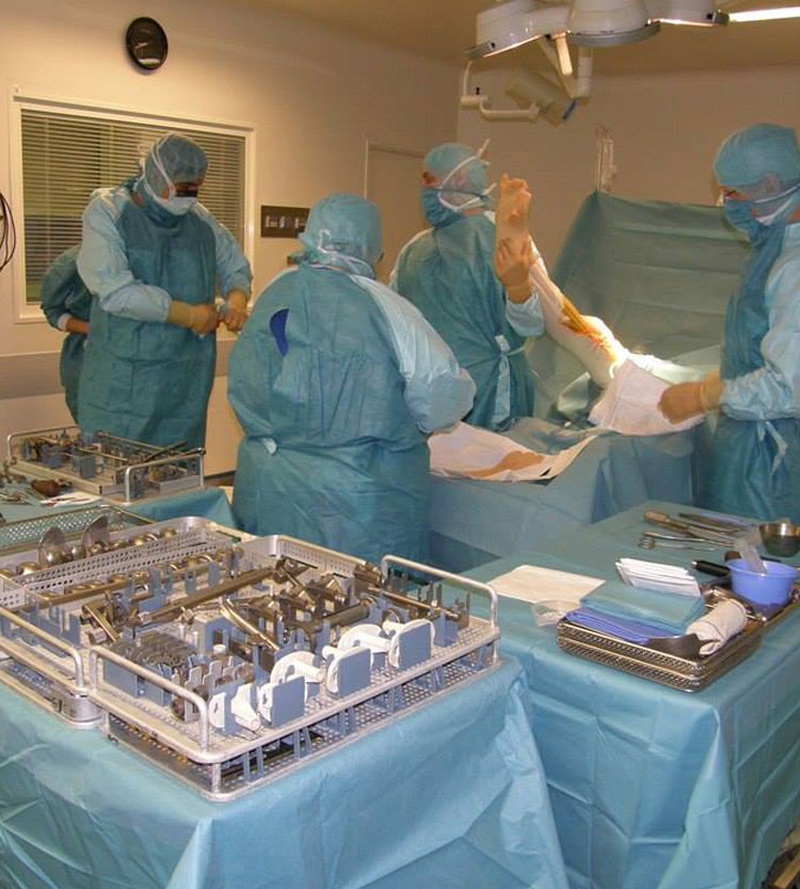
Surgery. In standard cases, the implantation of the artificial knee joint takes up to 1 hour. During the procedure, different measures are taken to prevent infectious complications. The first bandaging is done 24 hours after surgery. In the next period, once every 2-3 days. The removal of the sutures is usually 3 weeks after surgery.
Post-operative rehabilitation
Rehabilitation classes take place on the second day after surgery, which involve the presence of an exercise physician. The movements are active and passive, where the patient can start walking while being supported by a crutch. On the next day, the patient can start walking with cane support. After all the post-surgical procedure requirements, the patient can be sent to a rehabilitation center.
| Doctor | Name | Speciality | Work time (Saturday) |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Окрім Ілля Ілліч | Травматологія та ортопедія | - |
 | Васюк Сергій Володимирович | Травматологія та ортопедія | - |
 | Васильчишин Ярослав Миколайович | Отропед-травматолог | - |
Comments